The Impact of LinkedIn on the Recruitment and Staffing Industry
Introduction:
In the current digital age, LinkedIn has risen as a highly impactful platform that drastically affects the recruitment and staffing sector.
Exhibiting a vast spectrum of professionals from diverse fields, LinkedIn has revolutionised the technique through which organizations allure, assess, and bring in talent.
This article targets the investigation of LinkedIn’s impact on recruitment and staffing while highlighting the merits, difficulties, and upcoming trends intertwined with this commanding platform.
Overview of LinkedIn
Initiated in 2003, LinkedIn holds the title of being the largest professional networking platform worldwide.
With many registered members spanning diverse industries and professional levels, LinkedIn furnishes individuals with a platform to establish professional profiles, install connections with colleagues, and exhibit their skill sets and experiences.
It provides companies with a sphere to project their brand, job vacancies, and interact with likely candidates.
Presently, LinkedIn has evolved into a preferred platform for myriad professionals and organisations pursuing networking, recruitment, and prospects for career progression.
Here are some key statistics about LinkedIn as of 2024:
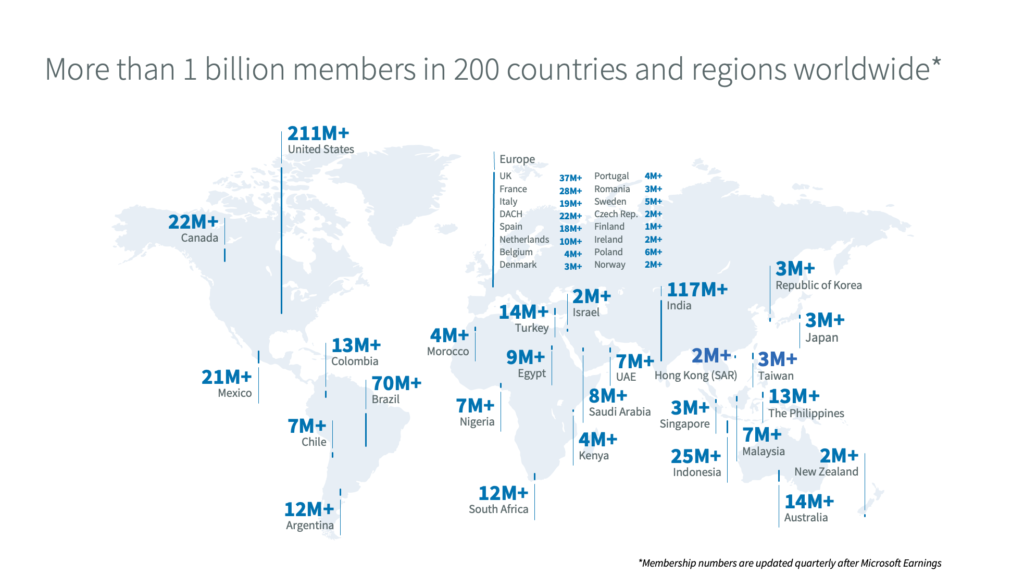
User Base: LinkedIn has over 1 billion members from 200 countries and regions worldwide. As of March 2023, over 900 million users were registered on the platform. Source
- 60% of LinkedIn users belong to the age group of 25 to 34 years. Source
- 42.8% of LinkedIn users are women, with 57.2% being men. Source
Revenue from Advertising: LinkedIn is expected to generate $6.79 billion through advertising in 2024. In 2022, the platform generated $5.13 billion. Source
Organisations on LinkedIn: There are 75 million organisations on LinkedIn, many of which use it for recruiting or as a media centre to publish news about their business. Source
Job Market: 49 million users look for jobs through LinkedIn. Source
Influencers and Decision-Makers: The platform has 180 million senior-level influencers, 65 million decision-makers, and 10 million C-level executives. Source
User Earnings: 60% of U.S. LinkedIn users earn $100,000/year. Source
Geographical Distribution: After the U.S. (211 million), the countries with the highest number of LinkedIn users are India (117 million), Brazil (70 million), and China (50 million). Source
Annual Revenue: LinkedIn’s annual revenue is $14.5 billion. Source
These statistics highlight LinkedIn’s significant role as a professional networking platform and its impact on the global job market and business networking.
Importance of Recruitment and Staffing Industry
The recruitment and staffing industry functions as a pivotal bridge linking job seekers to fitting job opportunities.
It assists companies in efficaciously identifying and procuring talented personas who bear the necessary skills and qualifications tailored for specific posts.
A sturdy recruitment and staffing industry ensures a functional job market while warranting organisations’ access to a wide array of competent candidates.
These insights provide a comprehensive view of the global recruitment and staffing sector, highlighting its size, economic impact, regulatory environment, and the influence of technology and market trends.
Market Size: The global Recruitment & Staffing market size was valued at approximately USD 505.97 billion in 2022. Source
Economic Impact: A study by Gallup found that low engagement costs the global economy $8.8 trillion annually. Source
Regulatory Landscape: The staffing industry is expected to experience a stable regulatory situation in 2024, following a few hectic years. Source
Employment and Social Outlook: The World Employment and Social Outlook report for 2024 highlights disparities between high and low-income countries, with higher unemployment and poverty rates in lower-income nations. Source
Recruitment and Tech Trends: By 2024, the global AI in recruitment market is projected to reach significant growth, reflecting the increasing integration of technology in recruitment processes. Source
Staffing and Recruitment Landscape: The staffing and recruitment landscape in 2024 reflects an increasingly digital, diverse, and dynamic world, necessitating businesses to stay ahead with new strategies. Source
US Staffing Industry: An overview of the US staffing industry for 2023 provides insights into the trends expected in 2024, indicating a dynamic and evolving sector. Source
Amidst today’s fierce business scenario, the recruitment and staffing industry becomes indispensable for organisations to preserve a skilled workforce and accomplish their strategic objectives.
Advantages of LinkedIn in Recruitment
LinkedIn plays an integral role in modern recruitment with its numerous benefits, making it indispensable for businesses seeking proficient candidates. Its prime virtue lies in its provision to connect with an expansive network of professionals.
- 140 Job applications are submitted every second on LinkedIn. Source
- 28 million people worldwide have added #OpeToWork frames to their profiles Source
- 61 million use LinkedIn to search for jobs each week. Source
- Users spend nearly 8 minutes on the platform. Source
Boasting over 1 billion users globally, LinkedIn presents to recruiters a significant number of potential candidates spanning varied sectors and geographical regions.
This platform enables companies to connect with an array of talent, which might be challenging to approach through conventional recruitment methods.
Access to a Large Pool of Professionals
The cornerstone of LinkedIn’s recruitment prowess lies in its outreach to an expansive network of professionals.
As the foremost professional networking platform worldwide, LinkedIn empowers recruiters to access an extensive array of candidates across different industries and geographical jurisdictions.
With its base of over 1 billion users, recruiters have an opportunity to engage with a diverse talent pool that might be inaccessible using other platforms.
This extensive accessibility amplifies the likelihood of sourcing highly skilled individuals in alignment with a company’s needs and objectives.
Enhanced Candidate Screening and Selection
LinkedIn also offers advanced candidate scrutiny and selection possibilities, facilitating recruiters to optimise their hiring process.
By implementing LinkedIn’s sophisticated search methodologies, recruiters can curate potential candidates using specific parameters such as job designations, industries, skills, and experience levels.
This targeted strategy saves both time and effort by concentrating on candidates who exhibit the necessary qualifications.
Moreover, LinkedIn profiles often feature recommendations, endorsements, and commendations from other professionals, offering valuable insights into a candidate’s expertise and credentials.
Cost-Effective Recruitment Method
One more advantageous facet of LinkedIn in recruitment is its cost-efficiency. When juxtaposed with traditional recruitment procedures, including job postings on job boards or print media, LinkedIn emerges as a more economical alternative.
These figures provide a general idea of the costs involved in hiring a candidate, which include various elements such as advertising, recruitment agency fees, staff time, and other related expenses:
- Average Cost in the US: The average cost per hire in the United States is approximately $4,700. This cost encompasses more than just placing an advertisement; it includes various aspects of the recruitment process. Source
- Range of Hiring Costs: The average hiring costs can range from $4,000 to $20,000 per new employee, depending on the role and level of the position. Source
- Cost for Executive Positions: For executive positions, the average cost per hire can be as high as $28,329. Source
- Glassdoor Study: According to a study by Glassdoor, the average cost of hiring an employee is around $4,000. However, this number can vary based on several factors. Source
- SHRM Research: The Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) indicates that the average cost of recruitment is nearly $4,700 per hire. Source
Businesses can establish a company LinkedIn page, publish job vacancies, and actively interact with potential candidates at a relatively lower cost.
This approach eradicates the necessity for pricey print ads, and minimises dependence on high-priced recruitment agencies.
LinkedIn’s pay-per-click advertising blueprint further grants companies the leverage to administer their recruitment budget and target their preferred audience productively.
Challenges and Limitations of LinkedIn in Recruitment
While LinkedIn provides various benefits for recruiting processes, it’s not without certain hurdles and limitations.
To make the best use of this platform’s resources, these roadblocks should be tactfully addressed.
The main challenges of LinkedIn in recruitment include the daunting volume of profiles and information, the trouble in authenticating candidates’ abilities and background, and the possible prejudice and partiality in the recruitment procedure.
Overwhelming Amount of Profiles and Information
A notable hindrance with LinkedIn is the overwhelming abundance of profiles and information at hand.
Due to the millions of professionals on the platform, the task faced by recruiters to sift through numerous profiles to identify the right candidate can be quite formidable.
This not only consumes a significant chunk of time but also complicates the task of identifying the most apt individuals for specific job vacancies.
To overcome this challenge, recruiters should construct thought-out search strategies and employ advanced filters to refine the screening process and pinpoint the most suited profiles.
To aid in this process, LinkedIn’s AI algorithm processes and shortlists job applicants by matching candidates with suitable job opportunities. While the specific workings of LinkedIn’s algorithm are proprietary and not fully disclosed, several key principles and features are known:
- Profile Data Analysis: LinkedIn’s AI analyzes the data in a user’s profile, including work experience, skills, education, and activity on the platform (such as posts and interactions). This comprehensive analysis helps in understanding the candidate’s professional background and interests.
- Job Description Matching: The algorithm compares the requirements listed in job descriptions with the qualifications of candidates. This includes matching job titles, skills, and experiences. The more detailed and accurate the job description and the candidate’s profile, the better the matching.
- Skill Endorsements and Recommendations: LinkedIn also considers endorsements and recommendations from other users. These peer validations can provide additional weight to the skills and experiences listed in a candidate’s profile.
- Applicant Preferences: The algorithm takes into account the preferences set by the candidates, such as desired industry, job location, and role type. This helps in aligning job suggestions with the candidate’s career aspirations and lifestyle choices.
- Engagement and Activity: Active users who regularly update their profiles, engage with content, and network on the platform may be more visible to the algorithm. Regular activity can signal a candidate’s current professional interests and engagement in their field.
- Learning and Adaptation: LinkedIn’s AI continuously learns from interactions on the platform. For example, when a recruiter skips over a candidate suggested by the algorithm, it learns from this feedback and adjusts future recommendations.
- Bias Reduction Efforts: LinkedIn has been working on reducing bias in its AI algorithms. This includes efforts to ensure that candidates are recommended based on their skills and experiences, rather than factors that could lead to unconscious bias.
- Recruiter Tools and Filters: Recruiters using LinkedIn have access to tools and filters that allow them to set specific criteria for candidates. The AI uses these criteria to shortlist candidates from the larger pool.
It’s important to note that while AI algorithms can significantly aid in the recruitment process, they are not infallible and should be used in conjunction with human judgment. Recruiters are encouraged to review AI-suggested candidates critically and consider a diverse range of applicants to ensure a fair and effective hiring process.
Difficulty in Verifying Candidate’s Skills and Experience
Another hurdle in the recruitment process on LinkedIn is the troubles faced when trying to effectively authenticate candidates’ competencies and history.
Even though LinkedIn profiles do offer data about a candidate’s background, educational qualifications, and employment chronicle, there is a lack of a structured verification method.
Job applicants may sometimes resort to questionable tactics, lies, or even fraudulent activities to enhance their chances of securing a job. Here are some common examples:
- Exaggerating Qualifications: Applicants may inflate their educational qualifications or professional certifications, claiming degrees or certifications they haven’t earned.
- Falsifying Work Experience: This includes inventing job positions, extending the duration of previous employment, or fabricating achievements and responsibilities in past roles.
- Manipulating Employment Dates: To cover up employment gaps, some candidates might manipulate the start and end dates of their previous jobs.
- Fake References: Providing fake references or asking friends or family to pose as former employers or colleagues is another tactic.
- Lying About Reasons for Leaving: Applicants might provide false reasons for leaving their previous job, especially if they were fired or left under unfavorable circumstances.
- Omitting Negative Employment History: Some candidates might omit jobs where they had issues like poor performance, conflicts, or were terminated.
- Inflating Salary History: To negotiate a higher salary, candidates might lie about their previous earnings.
- False Claims of Skills or Abilities: Claiming to have skills or expertise in areas where they have little to no experience.
- Misrepresenting Language Proficiency: Overstating their ability to speak, read, or write in a foreign language.
- Falsifying Background Information: This includes hiding criminal records, bad credit history, or other personal information that might impact their job prospects.
- Plagiarism in Application Materials: Copying someone else’s resume, cover letter, or portfolio work and presenting it as their own.
- Using Ghostwriters for Assessments: Having someone else write their job application tests, essays, or even attend virtual interviews on their behalf.
- Misleading Claims About Job Offers: Claiming to have other job offers to pressure a company into making a quick decision or offering more favorable terms.
- Faking Illness or Personal Circumstances: To get extensions for application deadlines, interview dates, or to explain gaps in employment.
Recruiters are often left to depend solely on the narrative provided by the candidates, which might be embellished or misrepresented.
This verification deficit may complicate the accurate assessment of a candidate’s skills, influencing their suitability for a given role.
Potential Bias and Discrimination in Hiring Process
The implications of LinkedIn on the recruitment sector also raise legitimate qualms about potential tendencies towards bias and discrimination during the hiring procedure.
Despite efforts to foster equal opportunity, subconscious biases might still pervade the recruiters’ judgement.
LinkedIn profiles offer personal details like the candidate’s photo, age, and even hobbies, which could unintentionally sway the selection procedure.
Recruiters, without adequate awareness and instruction, may inadvertently make decisions based on irrelevant aspects rather than focusing purely on the candidate’s qualifications and abilities, threatening the principle of fair recruitment practices that organisations aim for.
LinkedIn, like many companies using AI for recruitment and professional networking, has been aware of the potential for biases in their AI algorithms. These biases can stem from various sources and manifest in different ways:
- Historical Bias: If the data used to train the AI system reflects historical biases or inequalities, the AI might perpetuate these biases.
For example, if past hiring data shows a preference for candidates from certain universities or companies, the AI might favor similar candidates in the future. - Algorithmic Bias: The way an algorithm is designed can introduce bias. For instance, if an algorithm gives more weight to certain profile features over others, it might inadvertently favor certain groups of users.
- User Interaction Bias: The behavior of users on the platform can influence the AI. For example, if certain types of profiles or posts receive more engagement or endorsements, the AI might prioritise similar profiles or content, potentially marginalising less engaged users.
- Bias in Job Ads: AI systems used for job ad targeting can sometimes reflect or amplify societal biases, potentially leading to certain demographics being underrepresented in job ad viewership.
LinkedIn has been actively working to address and mitigate these biases. Some of their efforts include:
- Diverse Data Sets: Ensuring the data used to train AI systems is diverse and representative of the global workforce.
- Algorithm Auditing: Regularly auditing algorithms for signs of bias and making adjustments as needed.
- Inclusive Features: Implementing features that promote inclusivity, such as the option for users to provide pronouns or participate in diversity initiatives.
- Transparency and User Control: Providing users with more control over the data they share and how it’s used, and being transparent about how AI systems make decisions.
Despite these efforts, it’s important to recognise that completely eliminating bias in AI systems is a challenging and ongoing process. Users and recruiters are encouraged to be aware of these potential biases and use LinkedIn’s tools critically and thoughtfully.
Impact of LinkedIn on Staffing Agencies
The ascendance of LinkedIn has led to dramatic shifts in the conventional workings of staffing agencies.
By establishing a unique platform where recruiters can directly engage with potential recruits, LinkedIn has been instrumental in removing any necessity for middlemen.
The recruitment routine has been streamlined, enabling staffing agencies to connect with an expansive pool of experts and expedite the process of recruiting suitable applicants.
In addition, LinkedIn’s refined tools for candidate evaluation and selection simplify the task of gauging a candidate’s skills and experience, resulting in improved precision in aligning applicants and available positions. This effect, in turn, increases the quality of assignments made by staffing agencies.
Changes in Traditional Staffing Practices
LinkedIn’s emergence has been a catalyst for significant alterations in traditional staffing processes.
Before LinkedIn, staffing agencies leaned heavily on networking, relying on referrals and their internal databases to source potential candidates.
However, LinkedIn’s arrival opened a gateway to a large pool of professionals across varied industries and locations.
This has brought forth the need for staffing agencies to realign their strategies to this evolving digital terrain and to optimise LinkedIn’s capabilities to preserve its competitive edge.
Increased Competition and Market Dynamics
The influence of LinkedIn on the staffing sector has ushered in heightened competition and shifted market dynamics.
In providing employers with a medium to directly communicate with professionals, LinkedIn has challenged the conventional role of staffing agencies acting as intermediaries.
Employers now have the alternate option to contact potential candidates directly, thereby reducing their dependency on staffing agencies.
This has amplified the competitive environment among agencies, compelling them to offer distinct value propositions and to establish their specialisation in specific industries.
Additionally, these market dynamics necessitate that staffing agencies create a robust presence on LinkedIn and exploit its tools to sustain their relevancy and competitiveness.
Role of LinkedIn in Talent Acquisition and Retention
LinkedIn’s pivotal role in talent acquisition and retention for staffing agencies cannot be overstated. With a massive user base of professionals who are actively exploring new career opportunities, LinkedIn presents a huge reservoir of potential candidates that staffing agencies can access.
Moreover, LinkedIn grants invaluable insights into a candidate’s history, abilities, and experience, thereby enabling agencies to make well-informed hiring decisions.
Additionally, the networking possibilities provided by LinkedIn allow staffing agencies to foster relationships with both passive and active candidates, thereby heightening the likelihood of successful placements.
Moreover, LinkedIn’s capabilities allow staffing agencies to establish talent communities and engage with professionals, fostering continuous relationship management and facilitating long-term talent retention strategies.
Future Trends and Opportunities in LinkedIn Recruitment
As LinkedIn continues to morph and grow, there are several budding trends and promising possibilities predicted within the recruitment field.
A notable prospect is the incorporation of sophisticated technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into the platform’s infrastructure.
Harnessing AI and ML can reform the recruitment process, simplifying tasks such as screening candidates, interpreting resumes, and intelligently matching talent, freeing recruiters to concentrate on more strategic recruitment tasks.
Furthermore, LinkedIn is poised to offer a more personalised job search and career development experience, courtesy of AI algorithms.
These would present job recommendations tailored to a user’s unique skills, experience, and interests, enhancing the job search, and boosting the chances of finding a suitable fit for both job hunters and employers.
Moreover, employer branding is predicted to become a more prevalent function of LinkedIn, affording companies the opportunity to broadcast their culture, values, and employee experiences, cultivating a potent employer brand and drawing in top-tier talent.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The amalgamation of AI and ML into LinkedIn’s recruitment processes presents a multitude of benefits.
The ability to sift through and analyse sizeable data sets efficiently and effectively is possible through AI and ML, a boon for recruiters searching for the perfect candidates.
These technologies can also supercharge candidate screening tools by automating the evaluation of resumes, competencies, and credentials, and even foresee a candidate’s potential success through past data and trends.
Additionally, AI-based chatbots can enhance a candidate’s experience by supplying instant replies to queries and simplifying communication between recruiters and job seekers.
ML could further refine job ad effectiveness by targeting the most suitable audience and tailoring the content based on user interaction metrics.
On the whole, the amalgamation of AI and ML within LinkedIn recruitment could offer significant time and cost efficiencies while elevating the quality of candidate selection.
Personalised Job Recommendations and Career Development
The future trajectory of LinkedIn greatly revolves around providing personalised job matchmaking and fostering career advancement.
Relying on strong AI and ML capabilities, the platform can deliver customised job opportunities tailored to individual skills, experiences, and professional ambitions.
Through a sophisticated algorithmic approach, LinkedIn can dissect a user’s profile, credentials, and networking connections to recommend job openings with a high level of relevancy.
This specificity in job search can guide job seekers by whittling down opportunities most suitable for them.
Moreover, LinkedIn can offer career growth resources like digital courses, certification programs, and learning suggestions aligned with a user’s career aspirations and interests.
This bespoke support can play a pivotal role in helping users bolster their skills, delve into new professional territories, and stay abreast of trending industry patterns, thereby propelling their career progression.
Expansion of LinkedIn’s Role in Employer Branding
LinkedIn is projected to take on a more sizeable role in bolstering employer branding by offering companies a robust platform to articulate their brand and allure stellar talent.
Through features like company pages and employee testimonials, organisations can accentuate their culture, ethics, and distinctive offerings to prospective candidates.
With the vast user base and engagement LinkedIn boasts, businesses can tap into a deep pool of professionals and enhance their brand’s visibility.
By consistently sharing compelling content, such as industry insights, employee anecdotes, and company news, companies can present themselves as thought leaders and industry authorities, thereby fortifying their brand reputation.
Furthermore, LinkedIn’s targeted ad campaigns allow businesses to promote their employer brand to specific demographic and professional groups, ensuring their message gets the right eyeballs.
In summary, LinkedIn’s anticipated growth in employer branding will help companies distinguish themselves in a competitive job marketplace and draw the crème de la crème of talent to their teams.
Conclusion
LinkedIn has indubitably revolutionised the landscape of the recruitment and human resources.
This innovative platform has furnished recruiters with a vast array of professionals to connect with, streamlining the daunting task of finding ideal candidates.
Coupled with LinkedIn’s comprehensive profiles and user endorsements, the screening and selection process has seen a notable efficiency boost.
The platform’s cost-effective nature has transformed job posting from a financial burden to a widespread, accessible solution.
However, it’s fair to mention the challenges, such as sifting through colossal amounts of data and ensuring the validity of candidate’s skills based purely on their LinkedIn profiles.
Susceptibility to bias and discriminatory practices remains a concern due to the subjective evaluation of profiles.
These hurdles notwithstanding, the platform’s disruption to traditional staffing techniques, the competitive impetus provided to the industry, and the critical role it plays in acquiring and retaining talent are irrefutable.
The prospective integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning promises to further amplify LinkedIn’s already robust capabilities, through personalised job suggestions and professional growth opportunities.
Visionary foresight predicts an expanded role in employer branding, with companies portraying their ethos alongside vacancies.
In closing, whilst LinkedIn has radically modernized the recruitment sector and opened a realm of possibilities, it also presents some challenges that need to be acknowledged for the platform’s sustained success.
Committing an eye to the future, LinkedIn’s true potential may yet be untapped.
Ben Miranda.
LinkedIn Profile: https://www.linkedin.com/in/benito-miranda-sierra/
Articles in the Series:
LinkedIn Business Page: Maximising Your Brand’s Potential
LinkedIn Advertising: Getting Started
Best Time to Post on LinkedIn
LinkedIn Banner and Photos
How to Block Someone on LinkedIn
How to Delete Your LinkedIn Account
How to Cancel Your LinkedIn Premium Account
The Impact of LinkedIn on the Recruitment and Staffing Industry
References:
Kashyap, R. & Verkroost, F. C. J., 2021. Analysing global professional gender gaps using LinkedIn advertising data. EPJ Data Science.springer.com
Wheeler, L., Garlick, R., Johnson, E., Shaw, P. and Gargano, M., 2022. LinkedIn (to) job opportunities: Experimental evidence from job readiness training. American Economic Journal: Applied Economics, 14(2), pp.101-125.nsf.gov
Nguyen, L., 2021. The moral economy of the self: chasing the future with LinkedIn.lu.se
Punn, M., 2020. Impact of job seekers’ profile on social networking websites on recruitment process in indian it firms. MANTHAN: Journal of Commerce and Management.HTML
Kakavand, B., Teimourzadeh, A. and Kakavand, S., 2022. Organizational attractiveness: Targeting prospective employers on social networking sites. Human Systems Management, 41(6), pp.671-684.HTML
Drakopoulos, G., Kafeza, E., Mylonas, P. and Al Katheeri, H., 2020, November. Building trusted startup teams from LinkedIn attributes: A higher order probabilistic analysis. In 2020 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI) (pp. 867-874). IEEE.ntua.gr
Evsyukova, Y., Rusche, F., & Mill, W., 2023. LinkedOut? A Field Experiment on Discrimination in Job Network Formation.researchgate.net









